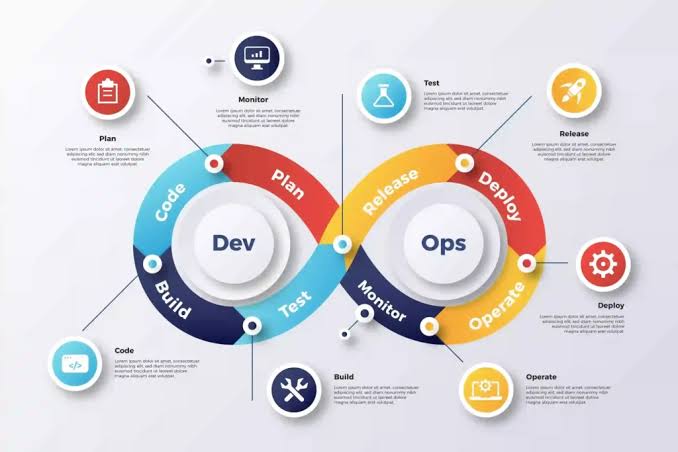
- In today’s fast-paced digital world, there has never been a greater demand for reliable and efficient software delivery. Traditional development methods’ incapacity to satisfy market expectations usually led to misunderstandings, inefficiencies, and delays. Introducing DevOps, a ground-breaking approach that optimizes the software lifecycle by combining development and operations. What is DevOps? The purpose of the technological and cultural movement known as “DevOps” is to integrate software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) by combining the phrases “development” and “operations.”
- Its primary goals are to increase deployment frequency, reduce development time, and automatically and continually deliver high-quality software. Instead of working in silos, DevOps encourages collaboration across functional boundaries, automation, continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD), and a shared responsibility for software reliability and performance. The Foundations of Collaboration and Communication in DevOps Through the removal of traditional barriers between teams, DevOps fosters an atmosphere of open communication and shared objectives. Throughout the whole process, from planning to execution and beyond, developers and IT specialists work together.
Automated
Manual activities can result in errors and slowdowns. DevOps’ focus on automation across the development, test, release, and deployment pipelines enables teams to operate more rapidly and precisely. Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) CI/CD is the foundation of DevOps. Continuous feedback and faster iterations are ensured via automated testing, regular integration, and seamless code production delivery. Observation and Contribution DevOps promotes real-time monitoring and ongoing feedback loops. This allows teams to improve performance, proactively address issues, and ensure that software meets user expectations. DevOps Advantages Faster Time-to-Marke
- Teams may learn, adjust, and get better over time with constant feedback.
Tools to Know in DevOps
- A number of ways are mostly used in a successful DevOps implementation. Among the important participants are:
Version control systems:
- GitLab, GitHub, and Git
CI/CD Pipelines:
- Azure DevOps, CircleCI, GitHub Actions, and Jenkins
Containerization:
- Kubernetes and Docker
- Prometheus, Grafana, and ELK Stack monitoring
Configuration Management:
- Chef, Puppet, and Ansible
Code for Infrastructure:
- AWS CloudFormation, Terraform
Adoption Challenges for DevOps
- Although there are many advantages, DevOps is not without its difficulties:
Cultural Resistance:
- It might be challenging to go from segmented teams to a collaborative culture.
Tool Overload:
- Selecting the appropriate stack can be difficult with so many tools accessible.
Security Issues:
- Secure coding and infrastructure techniques must be balanced with quicker deployments.
Concluding remarks
- DevOps is more than simply a set of tools; it’s a cultural movement that brings people, technology, and processes together to work toward a common goal: creating better software faster. Both startups and major organizations can greatly improve their agility, efficiency, and product quality by implementing DevOps practices. If you’re still experiencing delayed deployments or working in silos, now is the perfect opportunity to use DevOps and streamline your software development process.
Leave a Reply