The Impact of Sleep Deprivation on Health
In today’s fast-paced world, sleep is often sacrificed in favor of work, social obligations, and entertainment. While this trend may seem harmless in the short term, chronic sleep deprivation can have severe consequences for physical, mental, and emotional health. This blog explores the multifaceted impact of sleep deprivation on health and underscores the importance of prioritizing adequate rest.
Understanding Sleep Deprivation
Sleep deprivation occurs when an individual fails to get the recommended amount of sleep, which varies by age. Adults typically require 7-9 hours of sleep per night, while children and teenagers need even more. Sleep deprivation can be classified into two types:
- 1. Acute Sleep Deprivation: A short-term reduction in sleep, often lasting a few days.
- 2. Chronic Sleep Deprivation: Persistent lack of sufficient sleep over weeks or months.
Both forms of sleep deprivation can lead to significant health issues, even if the individual feels they have adapted to less sleep.
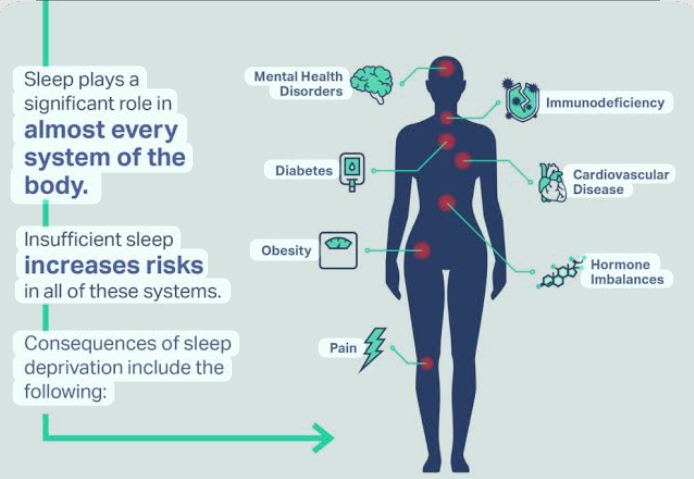
Physical Health Consequences
1. Cardiovascular Health:
Sleep deprivation increases the risk of hypertension, heart disease, and stroke. Insufficient sleep disrupts the regulation of blood pressure and inflammatory processes, straining the cardiovascular system.
2. Immune System Suppression:
Sleep is essential for a robust immune response. Chronic sleep deprivation reduces the production of cytokines, proteins that help combat infections, leaving the body more susceptible to illnesses.
3. Metabolic Dysregulation:
Sleep deprivation disrupts hormones that regulate hunger and appetite, such as leptin and ghrelin. This imbalance often leads to overeating and weight gain, contributing to obesity and type 2 diabetes.
4. Reduced Physical Performance:
Lack of sleep impairs muscle recovery and decreases endurance, strength, and coordination, making physical activities more challenging and increasing the risk of injury.
Cognitive and Mental Health Effects
1. Cognitive Impairment:
Sleep deprivation hinders memory consolidation, problem-solving abilities, and attention. It also slows reaction times, which can have serious consequences, especially for tasks requiring precision, such as driving.
2. Mental Health Disorders:
Chronic sleep deprivation is strongly linked to mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder. It can exacerbate existing conditions and make treatment less effective.
3. Emotional Instability:
Sleep-deprived individuals often experience heightened emotional reactivity, mood swings, and difficulty managing stress, which can strain personal and professional relationships.
Long-Term Consequences
The long-term effects of sleep deprivation extend beyond immediate physical and mental health concerns. Persistent lack of sleep is associated with:
1. Neurodegenerative Diseases:
Research suggests that chronic sleep deprivation increases the risk of conditions such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease by impairing the brain’s ability to clear toxic waste products.
2. Chronic Conditions:
Diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular diseases are more prevalent among those with long-term sleep deficits.
3. Reduced Life Expectancy:
Studies indicate that individuals with chronic sleep deprivation are at higher risk of premature death due to the cumulative toll on the body.
Social and Economic Implications
Beyond individual health, sleep deprivation has broader societal and economic consequences:
1. Workplace Productivity:
Employees suffering from sleep deprivation often demonstrate reduced efficiency, increased absenteeism, and higher error rates, costing businesses billions annually.
2. Healthcare Costs:
Treating sleep-related health conditions places a significant financial burden on healthcare systems worldwide.
3. Public Safety:
Sleep-deprived individuals are more likely to cause accidents, particularly in industries like transportation and healthcare, where alertness is critical.
Tips for Improving Sleep Quality
Recognizing the importance of sleep is the first step toward better health. Here are some practical tips to improve sleep quality:
1. Establish a Consistent Sleep Schedule:
Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day, even on weekends.
2. Create a Sleep-Conducive Environment:
Ensure your bedroom is dark, quiet, and cool. Invest in a comfortable mattress and pillows.
3. Limit Screen Time Before Bed:
Avoid electronic devices at least an hour before bedtime, as blue light can interfere with melatonin production.
4. Watch Your Diet:
Avoid heavy meals, caffeine, and alcohol close to bedtime.
5. Exercise Regularly:
Engage in physical activity during the day, but avoid intense workouts close to bedtime.
6. Manage Stress:
Practice relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, or journaling to calm your mind before sleep.
Conclusion
Sleep is a fundamental pillar of health, as vital as nutrition and exercise. Chronic sleep deprivation not only undermines physical and mental well-being but also affects society at large through reduced productivity and increased healthcare costs. Prioritizing and safeguarding sleep is essential for leading a healthier, happier, and more productive life. Remember, the hours you invest in sleep are an investment in your overall well-being.
The blog has been created with a detailed exploration of sleep deprivation’s effects on health. Let me know if you’d like to refine it further or add specific details!
Leave a Reply